
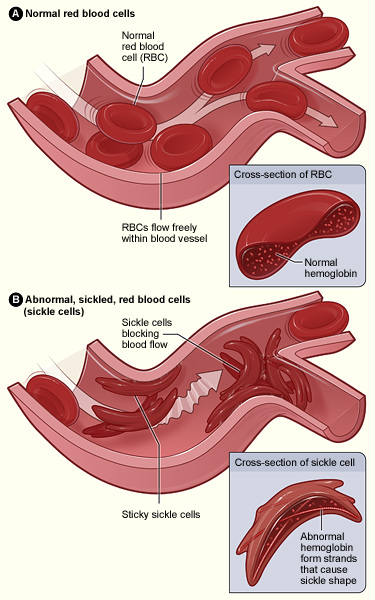
When considering a low mean corpuscular volume (MCV) in the evaluation of a patient, concurrent iron deficiency anemia should be ruled out.

Hemoglobin electrophoresis must always be interpreted while keeping the patient’s clinical picture in mind. Classic clinical and laboratory findings in hemoglobin electrophoresis in sickle cell hemoglobinopathies. 3Īt our institution, HPLC is often employed as the second method of electrophoresis to confirm a finding seen by capillary electrophoresis. It is suitable and effective for settings in which quantification is important such as assessing HbS and HbF percentages in individuals who are receiving a transfusion or hydroxyurea therapy for SCD. The time hemoglobin takes to eluate is referred to as the “retention time” this is detected by light absorbance. HPLC: This method has become increasingly popular since it can detect more types of hemoglobin than gel electrophoresis can. Abnormal hemoglobin capillary electrophoresis showing sickle cell disease with a significant peak seen in the HbS zone.ģ. The 15 different zones can be seen in the X-axis at the top of the chart.įigure 3.
Normal hemoglobin electrophoresis in an adult by capillary electrophoresis. The hemoglobin separates and is represented in the form of 15 zones. Capillary electrophoresis: An electric current is applied to a capillary made of silica, creating a flow of the buffer solution from the positively charged anode toward the negatively charged cathode. The different zones on an alkaline gel electrophoresis.Ģ. 1Ībbreviations: HbA, hemoglobin A HbS, hemoglobin S HbF, hemoglobin F HbA2, hemoglobin A2 HbC, hemoglobin C.įigure 1. HbA2 is the most negatively charged and moves only very slightly away from the anode. HbF has a slightly lower positive charge than HbA. HbA is the most positively charged among the normal adult hemoglobin types and moves the farthest toward the cathode. Common hemoglobin types and the lane where it is present in alkaline medium In the alkaline medium, there are four main lanes, as described in Table 1.
The charge carried by the globin protein is determined by the polypeptide chains that constitute the make-up of the protein. The separation of the hemoglobin depends on the charge that the globin protein carries. Gel electrophoresis: A hemolysate prepared from the blood is subjected to an electric field in both an alkaline and an acidic medium. These include gel electrophoresis, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), capillary electrophoresis, and isoelectric focusing. The first method is used to screen the provided sample, and the second method confirms the diagnosis if the first method detects an abnormality. To analyze the types of hemoglobin present in a blood sample, the standard of care involves using two methods of analysis on each sample. A hemoglobinopathy evaluation is a group of tests that determines the presence and relative amounts of abnormal forms of hemoglobin to screen for and diagnose a hemoglobin disorder. There are multiple methods to evaluate hemoglobinopathies such as thalassemia (decreased production of hemoglobin) and sickle cell disease (SCD hemoglobin variants).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
